During Glycolysis a 6 Carbon Sugar Diphosphate
Phosphofructokinase Is The First Regulator Of Glycolysis It S The Rate Limiting Step Of Glycolysis If I Have A Bunch Of Biochemistry Pharmacology Endocrine. What molecule provides the energy to produce 6-carbon sugar diphosphate.

Glycolysis Biology For Majors I
During glycolysis which of the following sets of molecules are formed from one six-carbon sugar diphosphate.

. Biology questions and answers. During glycolysis a 6 - carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3 - carbon sugar phosphate molecules. The initial step of lycolysis are the additions of two phosphates to glucose molecules at the expense of two molecules of ATP.
During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration during which glucose is modified to a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate and then split into two 3-carbon molecules. Each one of the 3-carbon sugar-phosphate molecules is converted through a series of reactions to pyruvate and hydrogen.
Glycolysis is the final step of cellular respiration during which glucose is modified to a 6-carbon molecule. TRUE Under aerobic conditions the end-product of glycolysis is further reduced to yield more ATP. During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules.
3The Krebs cycle turns three times for each glucose molecule. The result is a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule and 2 low energy adenosine diphosphate molecules or ADP. 1 NADH 1 ATP and 1 three-carbon pyruvate B.
During Glycolysis a 6 Carbon Sugar Diphosphate. During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar. Glycolysis takes place in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms and is the first step towards the metabolism of glucose.
Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy. Glycolysis is a catabolic pathway through which glucose C6H12O6 is oxidized to pyruvate CH3COCOO. Which one are correctDuring glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules.
The glycolytic sequence of reactions differs from one. During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. The two 3-carbon sugar molecules then both undergo another process to be turned.
TF During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. The two 3-carbon sugar molecules then both undergo.
Glycolysis Lecture 2 Biochimica. 4Oxygen is a product of the electron transport. This 6 carbon sugar-diphosphate molecule is being split into two 3-carbon sugar-phosphate molecules.
During a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules True Under aerobic conditions the end-product of glycolysis is. Moduler HSSILIIL Part 3 of 5 The purpose of the preparatory reaction is to break down so it can enter the citric acid cycle. Glycolysis occurs in preparation for cellular respiration making glucose to use during the rest.
Biology questions and answers. Afterwards the 6-carbon sugar diphosphate is split into two 3-carbon sugars by the enzyme Isomerase. Glycolysis is the central pathway for the glucose catabolism in which glucose 6-carbon compound is converted into pyruvate 3-carbon compound through a sequence of 10 steps.
During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. Pyruvic acid and hydrogen ions.
During the first steps of glycolysis 2ATP molecules are used to attach two phosphates to the glucose molecule leaving a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate and 2 ADP molecules. Glycolysis Only Continues With Hydrogen Removal. Multiple Choice O pyruvate carbon dioxide O acetyl coa pyruvate Part 4 of 5 During glycolysis a 6 carbon suga diphosphate molecule is split into two 3 carbon sugar phosphate molecules True False.
During the first steps of glycolysis 2ATP molecules are used to attach two phosphates to the glucose molecule leaving a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate and 2 ADP molecules. During glycolysis a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate molecule is split into two 3-carbon sugar phosphate molecules. 2 NADH 2 ATP and 1 three-carbon pyruvate.
So glycolysis produces ATP but also two byproducts. 2Under aerobic conditions the end-product of glycolysis is further reduced to yield more ATP. By Ra_Addyson64 13 Apr 2022 Post a Comment.
It takes place in the cytosol of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. True TF Under aerobic conditions the end-product of glycolysis is further reduced to yield more ATP. Afterwards the 6-carbon sugar diphosphate is split into two 3-carbon sugars by the enzyme Isomerase.
During the first steps of glycolysis 2ATP molecules are used to attach two phosphates to the glucose molecule leaving a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate and 2 ADP molecules.

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

Learn About The 10 Steps Of Glycolysis Nursing School Problems Glycolysis Pathways Biochemistry

Glycogenesis Glycogenolysis Note 1st Step In Glycogenolysis Is Production Of Glucose 1 Phosphate Biochemistry Notes Biochemistry Biomedical Science

Gluconeogenesis Synthesis Of New Glucose Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Mcat Study
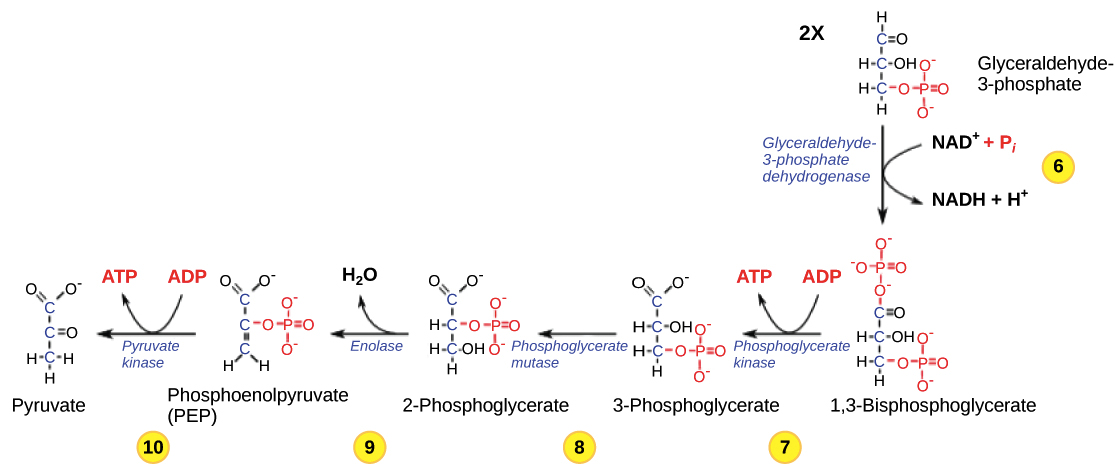
Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

Phosphofructokinase Is The First Regulator Of Glycolysis It S The Rate Limiting Step Of Glycolysis If I Have A Bunch Of Biochemistry Pharmacology Endocrine

Glycolysis Lecture 2 Biochimica Chimica Organica Ciclo Di Krebs

No comments for "During Glycolysis a 6 Carbon Sugar Diphosphate"
Post a Comment